How to Choose the Right Stainless Sanitary Fittings for Your Project
In the realm of industrial applications, the selection of the appropriate stainless sanitary fittings is pivotal for ensuring system integrity and hygiene. According to Michael Hart, a leading expert in sanitary engineering, "Choosing the right stainless sanitary fittings is not just about functionality; it’s about creating a safe and efficient environment for both products and personnel." This emphasizes the critical role that these components play in various sectors, especially in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology, where cleanliness and safety are paramount.
When embarking on a project that requires stainless sanitary fittings, there are several factors to consider. The materials used, the type of connections, and the overall design can significantly impact the efficiency and longevity of your system. It is essential to understand the specific requirements of your project, from the pressure rating to the chemical compatibility of the fittings. With the right guidance and knowledge, one can navigate through the multitude of options available in the market, ensuring that the selected fittings meet both the operational and regulatory standards.
Ultimately, selecting the right stainless sanitary fittings is a strategic decision that can enhance the reliability of your operations. With the expertise available in the field, project managers can achieve the best outcomes by making informed choices that contribute to the sustainability and hygiene of their production processes.

Understanding the Importance of Stainless Sanitary Fittings in Projects
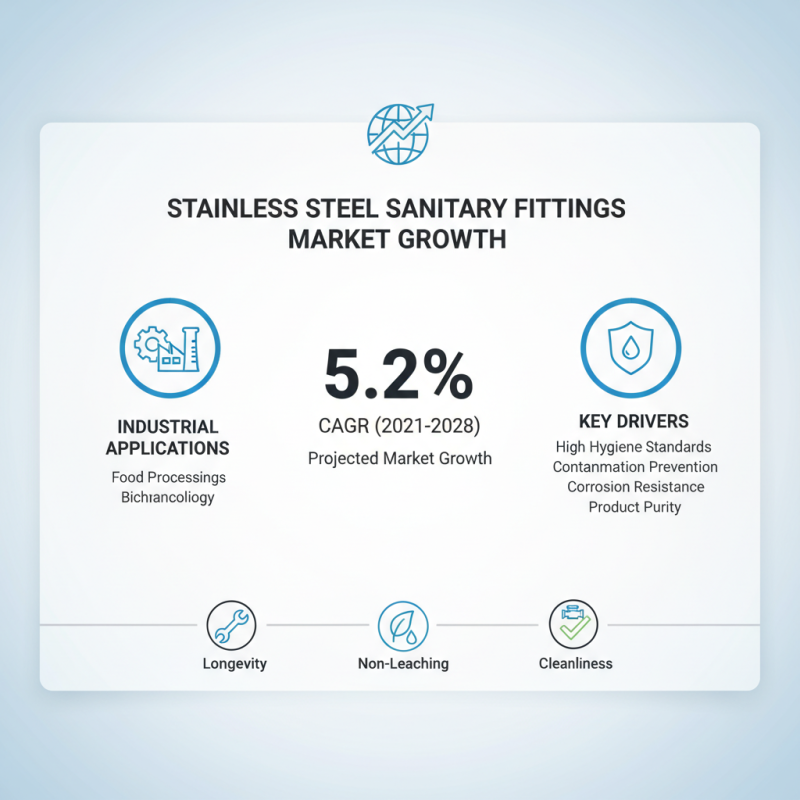
Stainless sanitary fittings play a crucial role in various industrial applications, particularly in industries that require high hygiene standards such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. According to a report by the Global Sanitary Fittings Market, the demand for stainless steel fittings is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is driven by the increasing focus on maintaining cleanliness and preventing contamination in production environments. The corrosion-resistant properties of stainless steel not only enhance the longevity of the fittings but also ensure that they do not leach harmful substances into products, which is paramount in sanitary applications.
Furthermore, the importance of selecting the right stainless sanitary fittings extends to functionality and compliance with industry standards. For instance, the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) outline specific regulations that components must meet to ensure safety and effectiveness in sanitary systems. Using the appropriate fittings can significantly impact operational efficiency and the overall success of a project. An emphasis on quality fittings reduces the risk of contamination and equipment failure, ultimately reflecting on the quality of the final product. In projects where sanitary conditions are imperative, making informed decisions about stainless fittings is essential for both regulatory compliance and consumer safety.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Stainless Sanitary Fittings
When selecting stainless sanitary fittings for a project, several key factors must be taken into account to ensure compliance, performance, and longevity. One of the primary considerations is the grade of stainless steel used in the fittings. According to the International Stainless Steel Forum, the most commonly utilized grades for sanitary applications are 304 and 316 stainless steel. Grade 316 is often recommended for environments exposed to corrosive elements, such as chlorine or saline solutions, due to its superior resistance to pitting corrosion. Therefore, assessing the chemical environment and potential exposure to corrosive substances is crucial in choosing the appropriate material grade.
Another essential factor is the fitting's design and its compatibility with the existing piping systems. Ensuring a proper fit reduces the risk of leaks and contamination in critical applications, such as food and beverage processing or pharmaceutical manufacturing. The European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group (EHEDG) emphasizes the importance of design cleanliness, which includes smooth surfaces and minimal dead legs to facilitate easy cleaning and disinfecting. Furthermore, considering the size, pressure ratings, and temperature tolerances of the fittings is vital to achieve optimal system performance and durability, reflecting the overall reliability of the piping system in demanding applications. Properly addressing these factors can lead to increased efficiency and a reduction in operational costs over time.
Types of Stainless Sanitary Fittings and Their Applications
When selecting stainless sanitary fittings for a project, it is crucial to understand the different types and their specific applications. Stainless steel is favored in the food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and biotech industries due to its durability, resistance to corrosion, and ease of cleaning. A report by the International Stainless Steel Forum indicates that the demand for stainless steel in sanitary applications is expected to grow at an annual rate of 6% over the next five years, reflecting its essential role in maintaining hygiene standards.
Common types of stainless sanitary fittings include elbows, tees, reducers, and clamps.
Elbows allow for changes in direction of piping, providing flexibility in design while minimizing pressure loss. Tees are used for creating branch lines in a pipeline, whereas reducers facilitate transitions between different pipe sizes.
According to a recent market analysis by Allied Market Research, the use of these fittings contributes significantly to system efficiency and helps prevent contamination in critical applications. The selection of the right type of fitting is vital for achieving optimal flow rates and maintaining product integrity, as improper fittings can lead to leaks and system failures.
Material Grades and Specifications for Sanitary Fittings
When selecting stainless sanitary fittings for your project, understanding material grades and specifications is crucial. Stainless steel comes in various grades, each offering distinct properties suitable for different applications in sanitary environments. The most common grades are 304 and 316. Grade 316, for instance, provides enhanced corrosion resistance due to its molybdenum content, making it ideal for use in environments exposed to harsh chemicals or saline solutions. According to the Stainless Steel Council, approximately 50% of all stainless steel produced globally is of 304 grade, highlighting its predominant use in sanitary fittings.
Tip: Always consider the environment in which the fittings will be used. For aggressive substances, opting for 316 grade may prevent future maintenance issues and enhance the longevity of your installation.
Specifications such as surface finish also play a pivotal role in the performance of sanitary fittings. A smooth surface finish, typically denoted as "Ra" (Roughness average), is critical for ensuring cleanliness and preventing bacterial harboring. Industry standards often recommend an Ra value of 32 microinches or lower for sanitary applications. According to the American Society for Quality (ASQ), a better surface finish can lead to improved washability and reduced contamination risk, which is essential for industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Tip: Evaluate the required surface finish based on the specific regulatory standards for your industry to ensure compliance and safety.
Material Grades of Stainless Steel Sanitary Fittings
This bar chart illustrates the most common material grades used for stainless sanitary fittings in various industries. It provides a comparison of the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of different grades.
Best Practices for Installation and Maintenance of Stainless Fittings
When it comes to the installation and maintenance of stainless sanitary fittings, following best practices is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. According to a report by the International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE), nearly 30% of facility downtime in the pharmaceutical sector can be attributed to inadequate maintenance practices. Proper installation begins with ensuring that the fittings are compatible with the system and made from materials that meet industry standards, such as the ASTM A270 for sanitary tubing. Furthermore, welding techniques should be performed by certified professionals to maintain the integrity of the joints, as improper welding can lead to contamination and system failure.
Maintenance of stainless sanitary fittings involves regular inspection and cleaning protocols. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends developing a routine inspection schedule to identify wear and tear, as well as potential contamination issues. Cleaning methods should align with the specific requirements of the application; for example, a Clean-in-Place (CIP) system is often employed in food and beverage processing to mitigate the risk of microbial contamination. Additionally, the use of non-abrasive cleaners is crucial to prevent surface damage, which can compromise the fittings and lead to costly replacements. By adhering to these best practices, operators can significantly enhance the reliability of their stainless sanitary systems and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Sanitary Fittings for Your Plumbing Needs
-

Why You Need a Comprehensive Sanitary Fittings Catalog for Your Projects
-

Why Sanitary Connectors Are Essential for Maintaining Hygiene in Food Production
-

Understanding the Types of Tubing Fittings for Optimal Performance
-

Exploring Fittings Steel Market Growth at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025 with Key Industry Insights
-

7 Best Practices for Choosing Sanitary Pipe Fittings for Your Business